V oversensing suspected
Case Summary
0 of 1 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the case before. Hence you can not start it again.
Case is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the case.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
Time has elapsed
Catégories
- Pas classé 0%
-
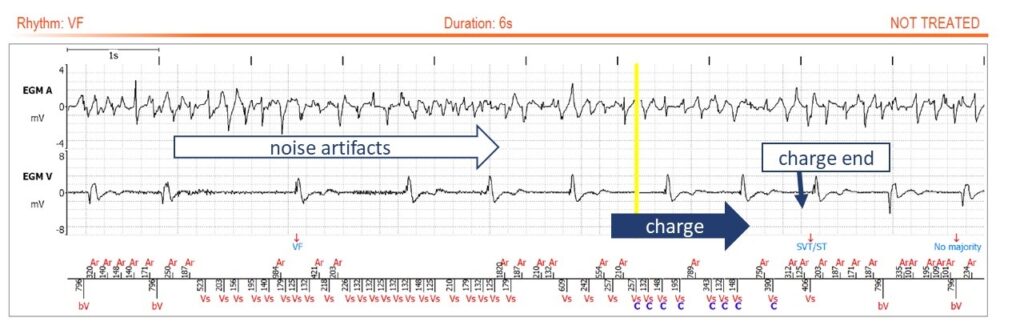
This transmission shows a “V oversensing suspected” alert, which is triggered when fast ventricular events (close to the blanking) are sensed, raising the suspicion of ventricular oversensing due to noise. Within the transmission, there is a VF episode without treatment, which is also very suspicious for intermittent oversensing. When we look at the EGM, we see the sudden onset of a low-amplitude and very fast noise, resembling a 50 Hz signal. As the majority of the ventricular events is VF also throughout the persistence, the diagnosis of VF is made and the ICD begins to charge. Just after the onset of the charge, the noise stops and the VF majority is lost, stopping the charge.
Next steps
One of the major advantages of remote medicine is the ability to contact the patient soon after the registration of asymptomatic, but possibly clinically relevent episodes. This is the case for atrial and/or ventricular arrhythmia, but perhaps even more so for oversensing of noise caused by lead dysfunction or external noise. In this case, there is a suspicion of external noise, detected by the sensitive ventricular ICD lead. This type of noise is most often caused by patient-machine interaction such as during manipulation of poorly isolated tools which are connected to the power grid. A context of wet surfaces may exarcerbate the problem (e.g. in the kitchen or in a flooded basement). When contacting the patient within a day of the event, it is often possible to identify the source. When the episode is discovered during an in-clinic consultation, often weeks or months have passed, making it very challenging and often impossible for the patient to remember the source which may have caused the lead noise. After identification of the problem, the source needs to be avoided by the patient (ideally repaired or replaced by other tools) in order to prevent inappropriate therapies. When the source cannot be identified, it is possible to exclude other sources of noise such as lead dysfonction or diaphragm oversensing. In this case, the patient was manipulating a switch board in a flooded basement.
- 1
- Current
- Review / Skip
- Answered
- Exact
- Inexact
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
ExactInexact