Real-time EGM 2
Case Summary
0 of 1 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the case before. Hence you can not start it again.
Case is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the case.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
Time has elapsed
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
-
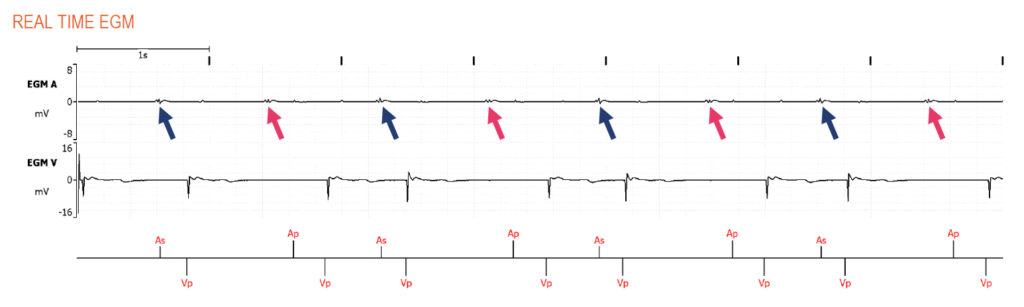
While the transmission does not display any alerts, examination of the real time EGM raises the suspicion of atrial undersensing.
EGM interpretation
We see a mixture of atrial sensing and atrial pacing, both followed by ventricular pacing, resulting in an irregular rhythm. The sensed atrial events are associated with low-amplitude signals which in fact reveal a regular atrial rhythm (sinus rhythm) which is half of the time not sensed. After each atrial undersensed event, there is atrial pacing which explains the irregular rhythm.
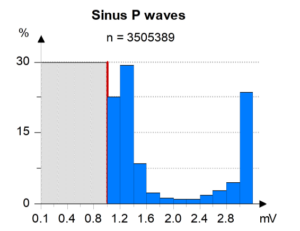
The pink arrows in the figure show the atrial undersensed events while the blue arrows indicate proper sensing of the atrial events. Atrial sensing is measured at 1.1 mV, very close to the programmed sensitivity of 1 mV. The sensing bar graph reveals that there are many sensed atrial events adjacent to the sensing threshold (the red line in the figure below), making it very likely that there is atrial undersensing, based on the bar plot alone.
Evaluation of risk
The clinical importance of atrial undersensing depends on the context. In a patient with CRT (most often not dependant), correct atrial sensing is imperative to ensure high %CRT delivery. Atrial undersensed events may be conducted to the ventricle before biventricular pacing, rendering the CRT ineffective. In a patient with an ICD, proper atrial sensing is required to correctly discriminate between supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias. Atrial undersensed events during a supraventricular tachycardia will direct the discrimination algorithms towards ventricular tachycardia (more ventricular events than atrial events), increasing the risk of inappropriate therapies. In patients with sinus node dysfunction undersensing of atrial events is less of a clinical problem since there are less or no spontaneous events and patients require atrial pacing. However, atrial undersensing may be a sign of lead dysfunction, associated with increase in capture threshold. In patients with AV block atrial undersensing is often asymptomatic at rest, but as the atrial rate accelerates, the undersensing often worsens and the ventricle is insufficiently accelerated, causing symptoms during exercise. In all patients with intermittent atrial undersensing, the ventricular response can be irregular, triggering symptoms such as palpitations.
Next Steps
The atrial myocardium is quite thin (a few millimeters at most) and therefore generates much less potential than the ventricle. Atrial undersensing is therefore not uncommon which is why the sensitivity on the atrial level is often below a millivolt. While lowering the sensitivity value below 1mV will greatly diminish the problem of atrial undersensing, it is associated with a greater risk of atrial oversensing. Atrial oversensing of intrinsic signals or low amplitude noise events may inhibit pacing temporarily and induce similar symptoms. In case of important symptoms, decrease in %CRT or increased risk of inappropriate therapies, the patient should receive a new atrial lead.
- 1
- Current
- Review / Skip
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
You receive the following transmission from a patient implanted with a dual chamber pacemaker due to paroxysmal AV block two years prior.
There is no alert within the transmission. What is the most probable diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect