1. VF Induction by T-wave shock (disabled)
Case Summary
0 of 1 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the case before. Hence you can not start it again.
Case is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the case.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 1 Questions answered correctly
Time has elapsed
Catégories
- Pas classé 0%
-
Tachogram
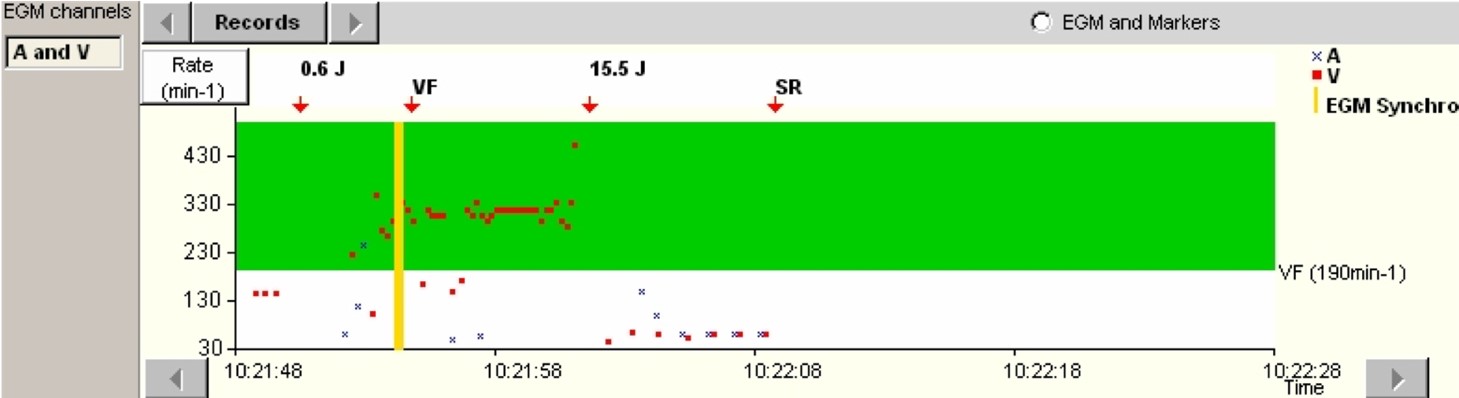
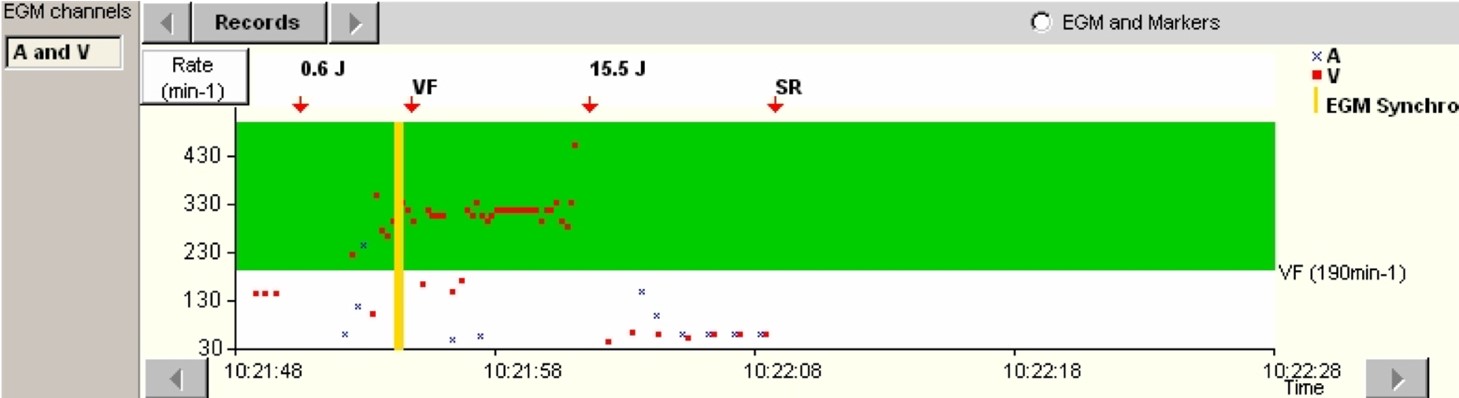
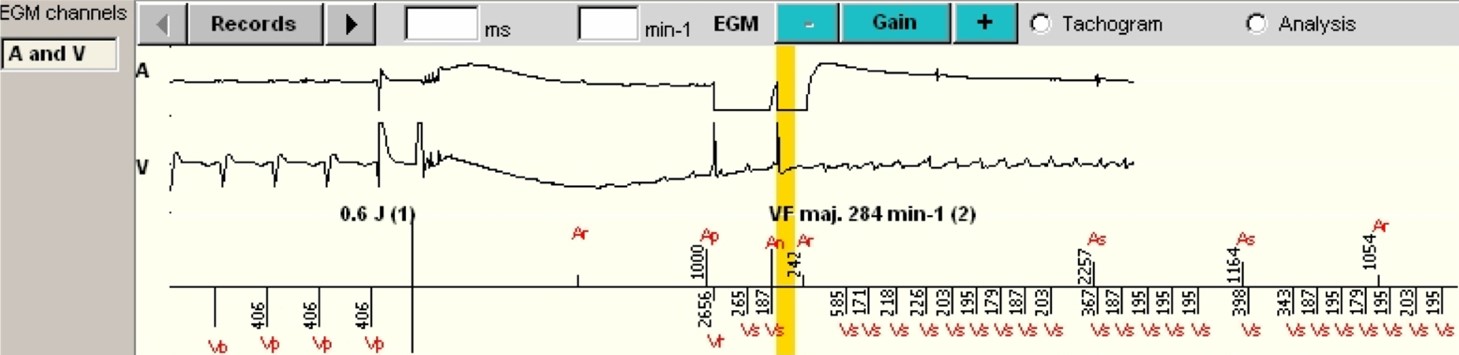
- The induction is carried out by a T-wave shock of 0.6 Joule after fixed rate ventricular pacing (Vp) to stabilize repolarisation. A 1-second blanking phase is applied after the shock, which explains the absence of apparent detection of ventricular and atrial events.
- A VF is diagnosed (VF and red arrow) with a very fast ventricular rate in the VF zone programmed at a starting rate of 150 per minute.
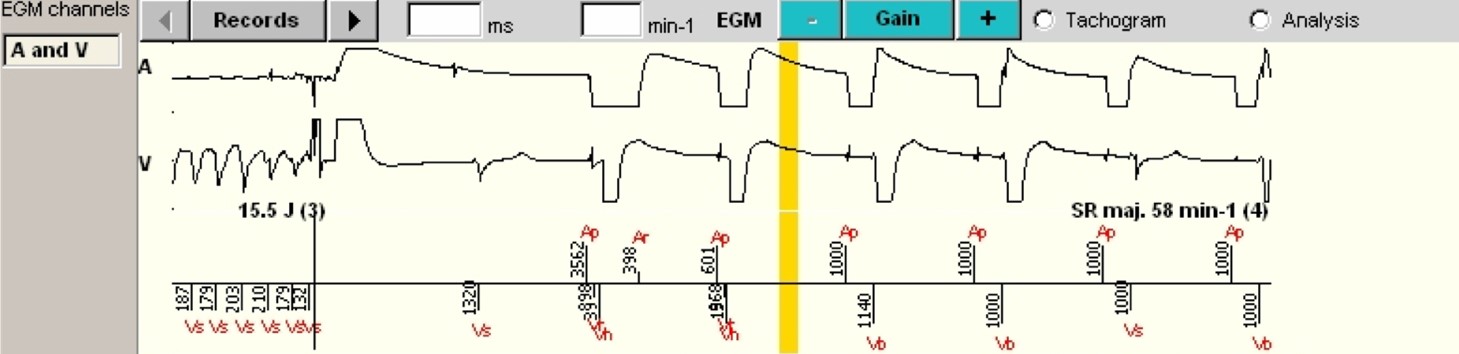
- After the charging of the capacitors, a shock of 15.5 Joule is delivered, with return to a slow, sinus rhythm (SR)
Electrogram
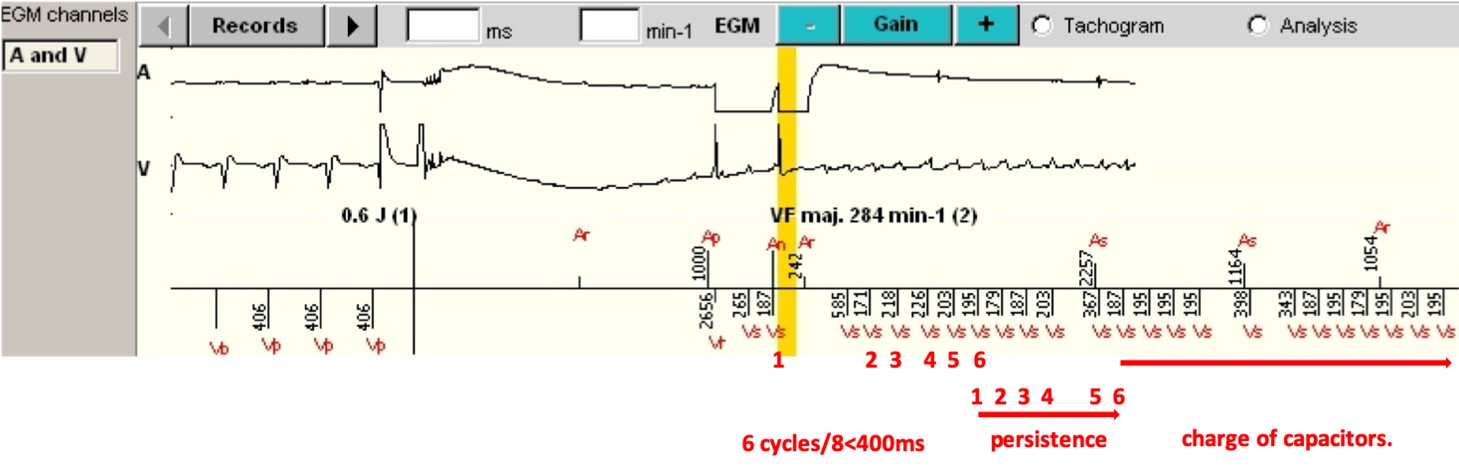
- To induce a VF, a shock of 0.6 Joule is delivered in the T wave of the last pacing cycle programmed at the rate of 150 per minute. A VF is indeed triggered.
- After a 1-second blanking period without detection, 75% of the ventricular cycles (6/8) are detected in the VF zone (i.e. 6 /8 cycles with a coupling interval < 400 ms), and a VF is diagnosed (vertical red arrow, VF maj. 284/min-1).
- The VF persistence begins, and the VF is validated as soon as the persistence threshold is reached. This diagnosis determines the type of triggered therapy, a charging of the capacitors. Thus, as soon as 6 sliding VF analyses are consecutively detected, the charge can begin. The VF remains perfectly detected and the charge continues.
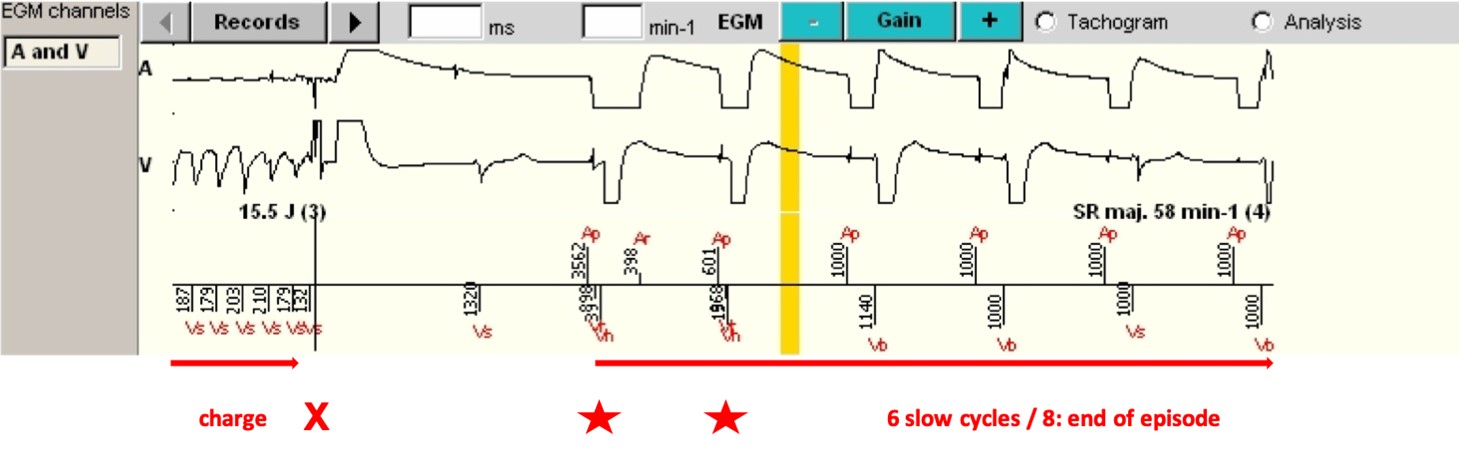
- Once the end of the charge is reached, the shock is delivered with an energy of 15.5 Joule on the next short cycle (red cross (X)) since the latter is in the VF zone, the majority analysis is still VF and the VF persistence counter is also still higher than the threshold at this time.
- After a 1- second blanking following the shock, the ensuing 6 out of 8 cycles are in the Slow zone, and the episode is terminated (SR maj. 58 min-1). The shock is deemed effective by the device.
- Of note (Vb, red asterisks), two ventricular paced cycles at the end of the safety window. It is likely that the energy of the end of the atrial spike and upon dissipation of the electric shock had accumulated, such that a ventricular detection occurred after the post-atrial ventricular blanking, which caused a pacing in the safety window.
Comments
This tracing illustrates the defibrillation test performed in the operating room at the end of the implantation procedure as well as the defibrillator’s behaviour in case of ventricular fibrillation. This example is based on a previous generation of devices with more basic information than with the modern defibrillators in order for the reader to understand the functioning of the device in a simple way.
The defibrillation test is used to verify the detection reliability of fibrillation F waves (this being the basic function of a defibrillator in order to achieve the required safety and effectiveness) as well as the quality of defibrillation with a typical safety margin of 10 Joules relative to the maximum energy delivered by the prosthesis.
- 1
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Exact
- Inexact
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
Patient
A 62-year-old man with ischemic heart disease and a history of myocardial infarction was implanted with an OVATIO DR 6550 dual-chamber model in secondary prevention after a sustained presyncopal VT episode.
Programming
The patient has just been implanted, and this is the induction of a VF to test the implanted system. The device was prepared with a VF zone starting at 150 per minute, with 6 persistence cycles, a first shock of 16 J followed by 34 J. Ventricular sensitivity was voluntarily set at 1.2 mV, hence degraded relative to what will be the definitive programming, in order to test detection in the most unfavourable conditions.
Tachogram
Memorized EGM
The tracing at the top is the atrial electrogram, underneath, the ventricular electrogram, lastly, at the bottom, the atrial markers above the line and ventricular markers below, along with the time intervals
What is your opinion? (multiple answers possible)
ExactInexact