Patient
Tracing
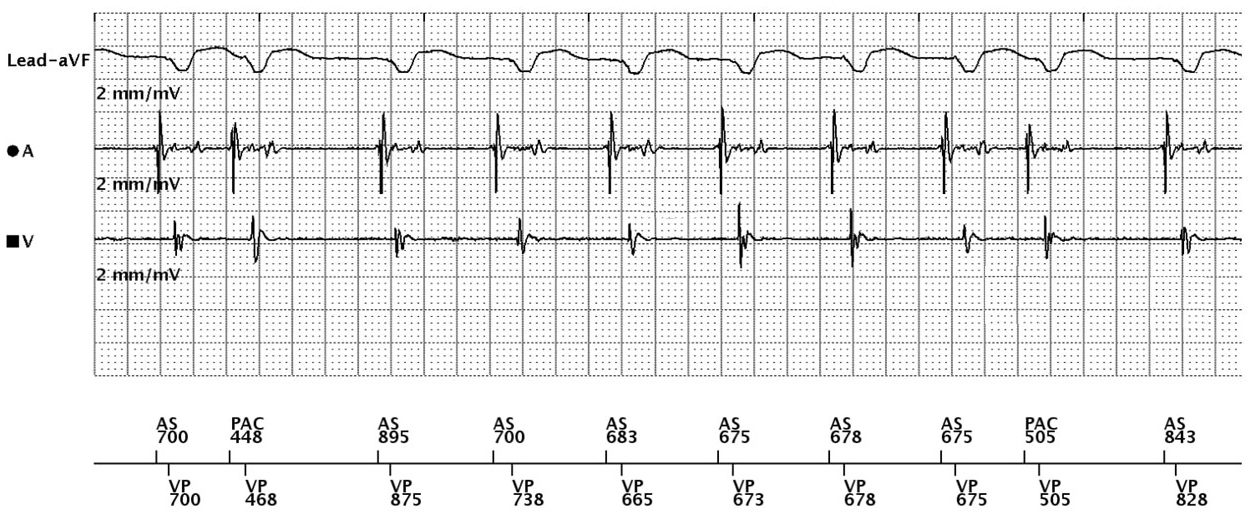
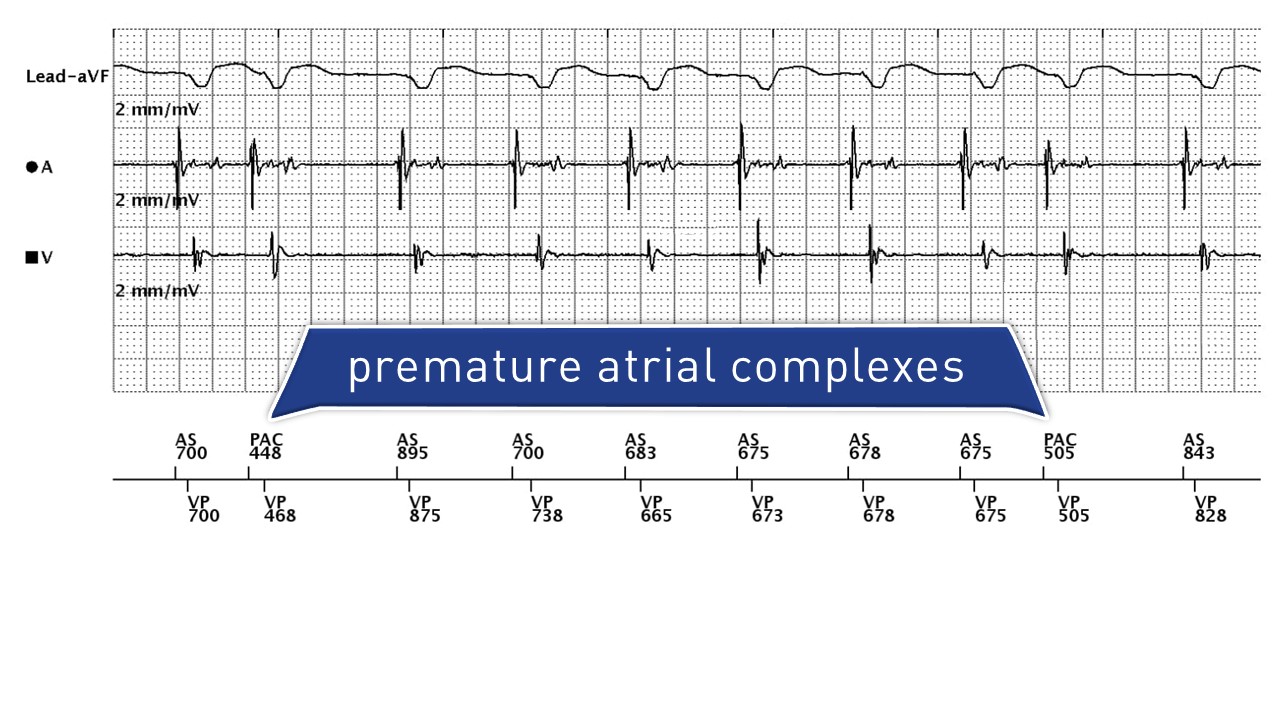
Tracing obtained on arrival
- atrial sensing and ventricular pacing (between 85 and 90 bpm)
- premature atrial contraction sensed outside any refractory period with compensatory pause
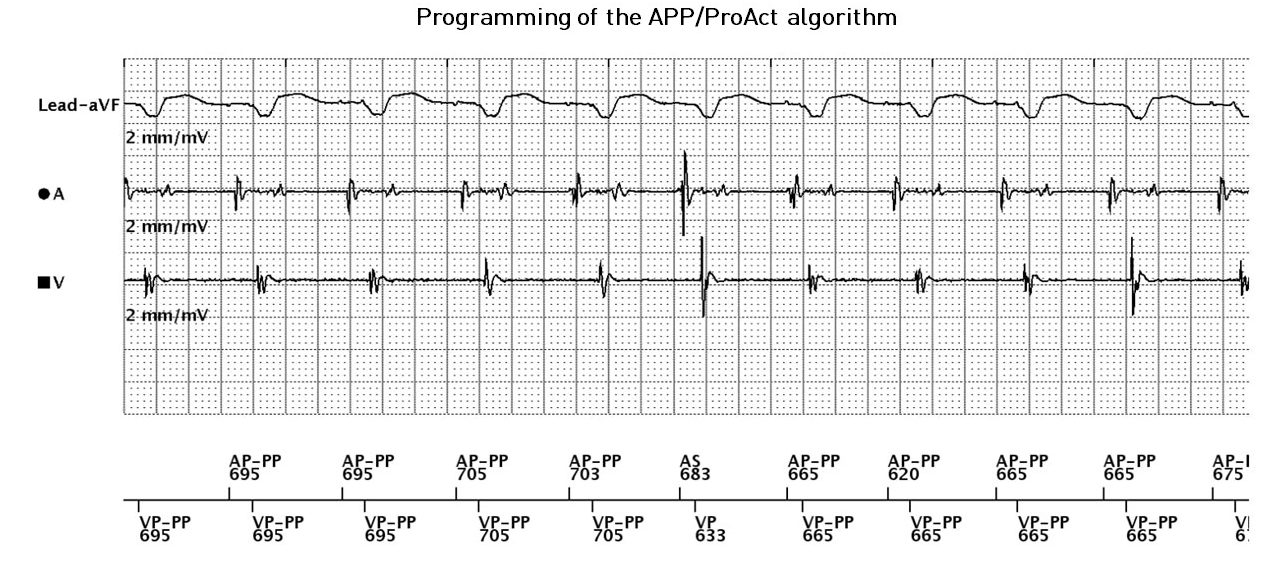
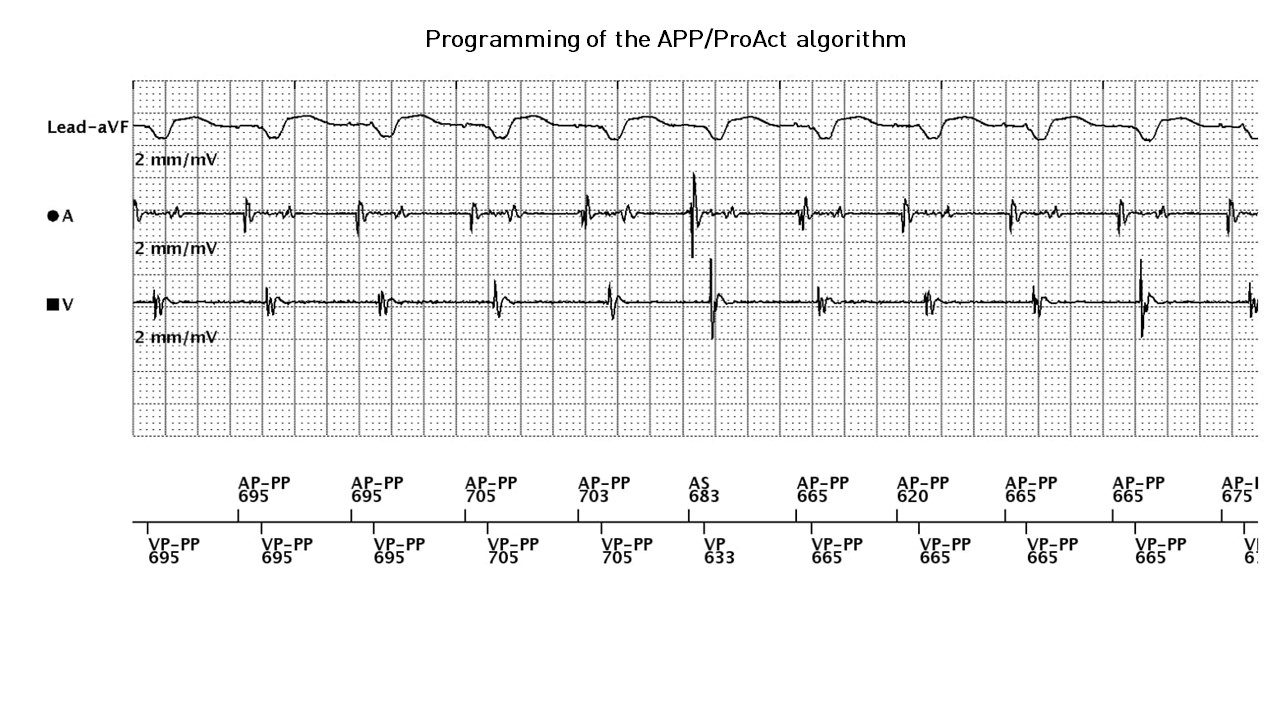
Programming of the APP/ProAct algorithm
- atrial and ventricular pacing at the rate imposed by this algorithm (AP-PP, VP-PP)
- premature atrial contraction
- acceleration of the pacing rate as a result of this atrial contraction
- gradual slowing of the pacing rate
Comments
- to trigger the onset of an atrial arrhythmia, 3 elements are generally required: a substrate, a context (sympathetic activation/parasympathetic activation ratio) and a trigger (most often a premature atrial contraction)
- pacemaker cannot interfere with the substrate or with the adrenergic context but may interfere with the occurrence of premature atrial contractions
- in Boston ScientificTM pacemakers, the ProAct algorithm increases the pacing rate following a premature atrial contraction in order to avoid successive short cycle – long cycle sequences
- the device measures the ventricular interval preceding the premature atrial contraction and applies a pacing interval to the next cycle corresponding to 75% of this interval
- the pacing rate is then gradually lowered to the lower rate limit by prolonging the pacing interval by 10 ms if 4 consecutive cycles occur without a premature atrial contraction
- the indicated APP/ProAct rate is limited by the value of the APP/ProAct maximum pacing rate
- effectiveness of this type of algorithm for preventing AF episodes has never been clearly demonstrated on large population samples and can lead to a feeling of tachycardia unfavorably felt by the patient