Tracing 2: Near shock
Time limit: 0
Case Summary
0 of 1 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the case before. Hence you can not start it again.
Case is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the case.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Case complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
Time has elapsed
Catégories
- Pas classé 0%
-
Interpretation
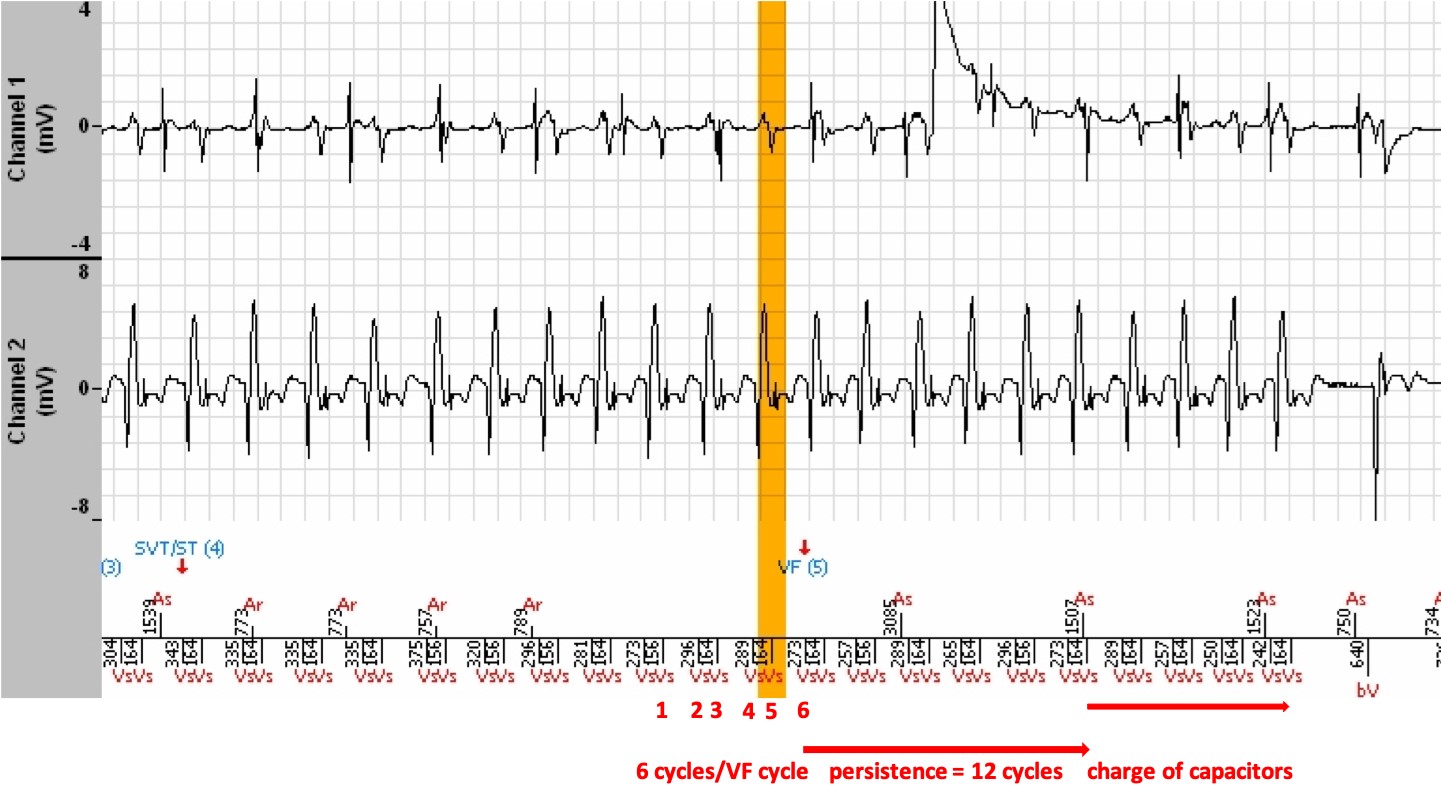
- In this example, the double railroad track pattern is much more pronounced because the episode is more prolonged, and the diagnosis of VF suggests a high risk of imminent shock that does not occur because, fortunately, a sufficient number of long cycles are detected which induce the suspension of the VF counter and of the therapies due to SVT/ST diagnoses.
- However, the diagnosis ends up being VF, which triggered the VF persistence and a start of capacitor charge. Fortunately, the episode terminates spontaneously and no shock is delivered.
The EGM

- This is indeed a ventricular tachycardia with double counting of the QRS as in the example of the first burst of this clinical case.
- A first diagnosis of VF is made because of the high rates due to double counting and a VF persistence is triggered. The latter exceeds the threshold of 12 programmed cycles and a charge of the capacitors has undoubtedly started, but which is not signalled by this platform previous to Platinium.
- The tachycardia subsequently slows down to a certain degree, which induces an alternation of shorter RRs and longer RRs, hence the SVT/ST diagnoses that appear since the ventricular rhythm is in the VT zone and unstable. The persistence is reset to zero in this situation.
- Thereafter, the tachycardia subsequently re-accelerates. A diagnosis of VF (VF marker (5)) is again made, and the persistence is again triggered. Due to the maintenance of the « tachycardia » rate in the VF zone, and a short programmed persistence of 12 cycles, a charge of the capacitors has undoubtedly started, but which is not signalled by this platform for the same reason given above.
- Fortunately, the ventricular tachycardia terminates spontaneously, such that the slow rhythm reappears, and the episode is ended.
Message
- The consequences of this double counting are catastrophic for several reasons.
- Shocks are initiated due to ventricular tachycardias that could otherwise be stopped by simple ATP sequences.
- Shocks are psychologically very poorly tolerated, even if the patient may have felt palpitations but probably no syncope.
- Iterative shocks may have a deleterious effect on the heart.
- Each charge will wastefully pump energy from the battery, at the cost of reducing the life of the device.
- The resolution of this problem is delicate and can only be surmounted by a prolongation of the post-ventricular ventricular refractory period, which is impossible on the Microport models, and which would seriously harm the detection capacity of very fast ventricular rhythms. Changing the ventricular sensitivity so as to not detect this double counting is also very dangerous and should not be applied! The persistence may be lengthened in hopes of a spontaneous termination of the burst, but if it is prolonged, it will not change the risk of shock. The answer is therefore only in a complementary solution aimed at ablating the circuit responsible for this monomorphic tachycardia, with the hope that the emergence of another tachycardia will not produce the same effect!
- 1
- Current
- Review / Skip
- Answered
- Exact
- Inexact
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
Patient
This is a patient implanted with a triple-chamber defibrillator with conventional criteria recommended for the indication. The QRS measured on the ECG is very wide at 180 ms. The patient has a fairly extensive sequela of anterior necrosis, and the RV defibrillation lead is placed in the mid anterior septum.
Tachogram
Statement
Slow cycles reset the VF counter and result in SVT/ST diagnosis
ExactInexact